To know how hearing aids work, we need to first understand the different parts of the hearing aids and their functions. Four essential components of all hearing aids are Battery door, Microphones, Receivers, and Buttons.
- Battery door: This is where you would place the battery. With a functional battery in and close the battery door, the hearing aid will be turned on. Once the battery door is open the hearing aids will be turned off. Hence the battery door also functions as the on and off button for the hearing aids.
- Rechargeable hearing aids: To turn rechargeable hearing aids on and off you would need to use the charger. With the hearing aids placed in the charger, the charger itself will turn off the hearing aids, and after you removed the hearing aids from the charger, the hearing aids will automatically turn itself back on.
- Microphones: The main function of the microphones is to pick up sounds from the environment, so sounds can be sent down and process through the processing chips that are located inside of the body of the hearing aids.
- Receiver: Another name for Receiver is Speaker. This is the part of the hearing aid that sits the closest to the eardrum, and this is where the amplified sounds come out of the hearing aids.
- Buttons: Buttons can function like volume control, or program changing button, or both. To determine the function(s) of the buttons, it will always be a discussion between you and your hearing health professionals.
As an overview, when sound in the environment gets picked up by the microphones it will get sent down and get processed by the processing chips that are located inside the body of the hearing aids and the amplified sound will get sent out by the receiver.
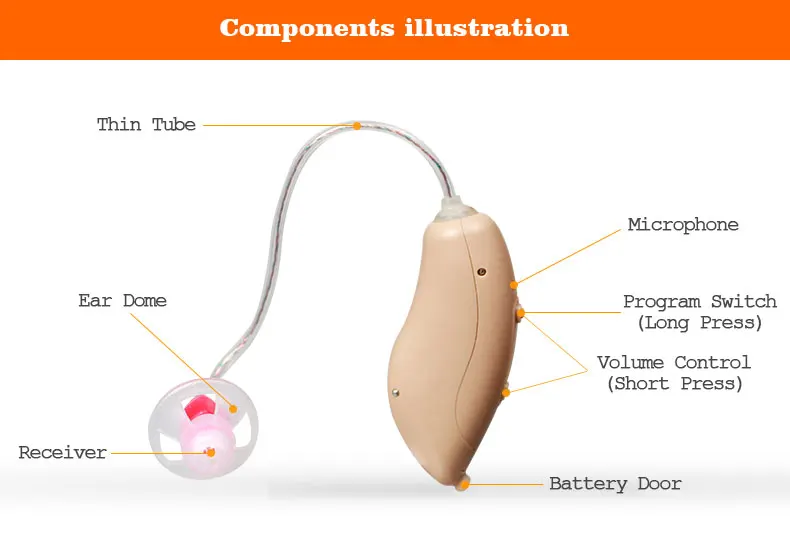
_________________________________________________________________________
Modern day digital hearing aids have three basic characteristics:
- They are all re-programmable.
- They all function automatically.
- They reduce background noises.
To fit an induvial with hearing aids, hearing test results are needed. Based on the severity or the degree of the hearing loss at each induvial tested frequencies or pitches, the hearing aids know how much amplification is needed to provide at each frequency. At frequencies where there is no hearing loss or minimum hearing loss, the hearing aids will provide no or minimum amplification. At frequencies where there is a significant amount of hearing loss, the hearing aids will provide more amplification to help the patient.
Once the hearing aids are on, microphones of the hearing aids will constantly be scanning the environment and pick up sounds in the environment. The hearing aids nowadays are smart to distinguish between speech and background noises, and the hearing aids will always automatically amplify any speech sounds in the environment (especially speech sounds that are present in the front of the individual) and reduce any background noises.
“Do hearing aids reduce background noises completely?”
The answer is “no.” Because that’s not how normal hearing works, with normal hearing sensitivity, we hear both background noises / environmental sounds and speech at the same time. However, the key is hearing aids will reduce background noises, amplify, and make speech more prominent for the wearer.

“How do hearing aids help to slow down the process of hearing loss?”
To fully process acoustic information, sounds have to make sense up at the brain. The ears are just functioning as a conducting system for sounds. To keep the hearing part of the brain active, sounds from the environment are essential. With hearing loss, less sounds are being sent up to the brain. Therefore, over time the hearing part of the brain progressively becomes less active. With longstanding untreated hearing loss, it will increase the rate to develop more severe degrees of hearing loss and brain atrophy could also occur to the hearing part of the brain. Once one part of the brain atrophies, it can spread to other parts of the brain over time. Therefore, dementia occurs.

